Manage page layouts
The page layout determines how a page is structured and divides it into different layout areas. Within these layout areas you can place any number of front end modules, which are executed one after the other when the page is called and HTML page code is generated for the web page. A front end module is also used to insert the articles, that is, the content.
If a page is not assigned a page layout, it inherits the page layout from a parent page. If no page layout is linked there either, the front end output is limited to a short “No layout specified”.
Structure of the front end
In order to be able to convert individual page layouts in the front end into a neatly arranged and above all cross-browser functional website, a powerful CSS framework is required, which is prepared for all eventualities. The compact Contao CSS framework fulfills this task very well. It automatically generates the basic structure of the website based on a page layout, which by default consists of up to three columns and an optional header and footer.
Header and Footer
Each page layout can have a header and a footer. Usually, the header contains the company logo, the footer contains copyright information and a link to the imprint and privacy policy.
lines: Here you add a header and footer to the layout.
Height of the header: Here you can set the height of the header.
Height of the footer: Here you can set the height of the footer.
Column configuration
By default, up to three columns are available. You can specify the width of the left or right column, the main column adjusts automatically.
Columns: Here you select the number of columns in your page layout.
Width of the left column: Here you define the width of the left column.
Width of the right column: Here you set the width of the right column.
Custom layout areas
By default, the Contao CSS framework defines the following layout areas:
- Header
- Left column
- Right column
- Main column
- Footer
With these five areas, most common page layouts can be easily implemented. However, there are some layouts that deviate from this classic division, such as those with an additional area under the header or a two-part main column.
To help with these page layouts Contao allows you to define additional layout areas in the back end settings and arrange them. Your own layout areas can be used in the page layout just like the standard areas.
Own layout areas: Here you activate your own layout areas.
Position of the layout areas: In connection with the standard fe_page page template, you can position your own layout areas as follows:
- Before the enclosing element
top - Below the header line
before - In the main column
main - Above the footer
after - After the enclosing element
bottom - Manual output
manual
Web Fonts
Here you can add one or more Google Fonts to your website. Once you have selected a web font, you can add it here by specifying the parameters Roboto:400,700.
Output in source code:
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Roboto:400,700" rel="stylesheet">
Manual integration of “web fonts” is recommended. Otherwise, you should follow the following instructions from Google: Get Started with the Google Fonts API, the “Google Fonts API Version 2” is currently not supported.
Then you can access the web font via your CSS file.
body {
font-family: 'Roboto', sans-serif;
}
Image sizes
This feature is available in Contao 4.8 and later.
With these settings you can define the image size for the lightbox in the page layout.
Image size for the lightbox: Here you can set the dimensions of the image and the scaling mode for the lightbox.
Pixel densities for the standard image: The image sizes are adjusted automatically. For example, the entry 1x, 1.5x, 2x generates the following HTML code:
<img srcset="img-a.jpg 1x, img-b.jpg 1.5x, img-c.jpg 2x">
Style sheets
Here you define which stylesheets are included in the page layout and in which order.
The components of the Contao CSS framework, internal stylesheets and external stylesheets are available.
Components of the Contao CSS framework: Here you can activate the components of the Contao CSS framework.
| Components | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Layout Builder | Creates the CSS layout based on the page layout settings. This component must be active for the page generator to work correctly! |
| Responsive layout | Adds a viewport tag to the header and scales the CSS layout based on the width of the device. |
| 12-column grid | Creates a responsive 12-column grid, which is offset12 controlled by the CSS classes grid1 to grid12 and offset1 to. |
| CSS reset | Removes the inconsistent standard formatting of HTML elements in different browsers |
| Forms | Basic formatting of form elements and buttons. |
| Icons | Basic icons for downloads and file attachments. |
Internal stylesheets: Here you can add internal stylesheets to the layout.
External stylesheets: Here you can add external CSS, SCSS or LESS files from the file system.
Loading order: Here you can set the loading order of the internal and external stylesheets.
Combine scripts: Here you can determine if the .css and .js files should be merged.
RSS/Atom feeds
Feeds embedded in a page layout are linked in the header area of the page and can be subscribed to directly in the address bar of most modern web browsers. The “header” is not the header of your page layout, but the <head> tag of the HTML source code.
News feeds: Here you can select the feeds from your news archives.
Calendar feeds: Here you can select the feeds from your calendars.
Front end modules
In this section, you assign the front end modules to the individual layout areas that are to be displayed on the page. The modules of each layout area are arranged one below the other in the order you specify.
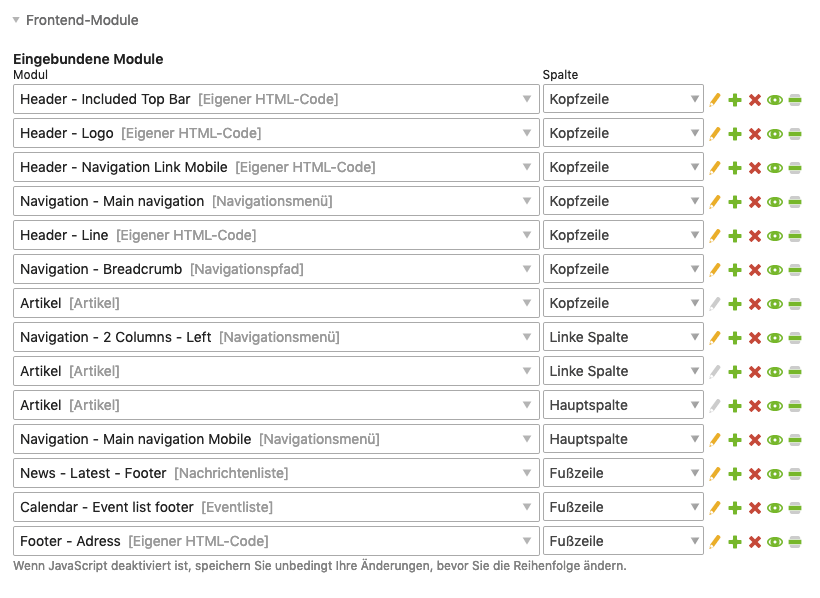
Integrated modules: Here you select the modules for the page layout.
JavaScript
The JavaScript templates, Analytics templates, External JavaScript and Own JavaScript code are available.
JavaScript templates: Here you can select one or more JavaScript templates.
| Template | Declaration |
|---|---|
| js_autofocus | If, for example, a field in a form is filled in incorrectly, this field will receive a <p> tag with the class “error” after it is submitted. The JavaScript ensures that the system automatically scrolls to this class. |
| js_highlight | This is a syntax highlighter for script languages, it is needed for the content element “Code”. |
| js_nocookie | In order for Contao to protect you from CSRF attacks, visitors must allow cookies. The template dynamically generates a message if a visitor has disabled cookies in his browser.
This feature is available in Contao 4.7 and later. |
| js_slider | Provides JavaScript for the content element “Content Slider”. |
Analytics templates: Here you can select the analytics template of Google Analytics and/or Matomo (Piwik).
To do this, one of the desired templates must be placed in the templates folder of the theme and provided with the Google Analytics ID or Piwik ID and Piwik URL.
/* Template: analytics_google.html5 */
$GoogleAnalyticsId = 'UA-XXXXX-X';
/* Template: analytics_piwik.html5 */
$PiwikSite = 0;
$PiwikPath = '//www.example.com/piwik/';
External JavaScripts: Here you can add external JS files from the file system.
Own JavaScript code: Here you can add your own JavaScript code, which will be displayed at the end of the page.
jQuery
Load jQuery: Add the jQuery library to the layout.
jQuery templates: Here you can select one or more jQuery templates.
| Template | Declaration |
|---|---|
| j_accordion | Provides the jQuery plugin for the content element “Accordion”. |
| j_colorbox | Provides the jQuery plugin for displaying images in large view (lightbox effect). |
| j_tablesort | Provides jQuery plugin for the sorting option of the content element “Table”. |
jQuery source: Here you can select from where the jQuery script should be loaded. The following three options are available:
- Local file
- CDN (code.jquery.com)
- CDN with local fallback
MooTools
Load MooTools: Add the MooTools library to the layout.
MooTools templates: Here you can select one or more MooTools templates.
| Template | Declaration |
|---|---|
| moo_accordion | Provides the MooTools plugin for the content element “Accordion”. |
| moo_chosen | With this MooTools plugin you can make long select menus clearer and more user-friendly. The select menu must be given the CSS class “tl_chosen”. |
| moo_mediabox | Provides the MooTools plugin for displaying images in large view (lightbox effect). |
| moo_tablesort | Provides MooTools plugin for the sort option of the content element “Table”. |
MooTools source: Here you can select from where to load the MooTools script. The following three options are available:
- Local file
- CDN (googleapis.com)
- CDN with local fallback
Static Layout
The CSS framework adjusts the page layout to the width of the browser window by default, which is also called “liquid layout”. In contrast, a static layout has a fixed width and is displayed in the center of your browser window, for example. In Contao, both layout types are supported.
Static layout: Here you define a page layout as static.
Total width: Here you can enter the total width of the website.
Alignment: Here you can set the alignment (left-aligned, right-aligned or centered) of the web page.
Expert settings
In the expert settings, you can change the page template that is used for the page layout, but you should only consider this if the Contao tools are not sufficient or if you want to use an external CSS framework. In most cases, however, you should be able to use the standard options without any problems.
Page template: Here you can select the page template.
Compress markup: Here you can determine whether the HTML markup should be compressed before sending it to the browser.
Viewport tag: Here you can set an individual viewport tag.
Example: The page should adapt to the viewport, but still allow scaling:
width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0
Output in source code:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
Title tag: Here you can overwrite the title tag.
Body class: Here you can assign a CSS class to the body tag of the HTML page and thus create format definitions for a certain page layout.
Body onload: Some JavaScripts require a so-called “Body Onload Event” to initialize the script when the page is loaded. If you want to use such a JavaScript, you can enter the required code here.
Additional <head> tags: In the header of your website, the meta information of the page is displayed and the included stylesheets and JavaScript are linked. Here you can add any additions and e.g. insert further stylesheets.